
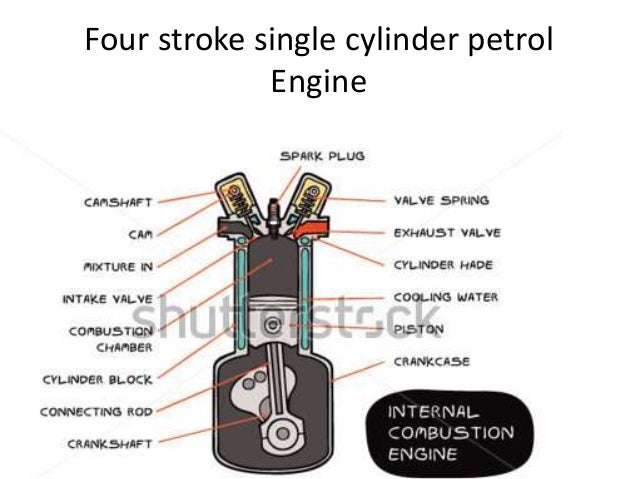
However, in general, gasoline engines convert 20% of the fuel (chemical energy) to mechanical energy in which only 15% will be used to move the wheels. The thermal efficiency of these gasoline engines will vary depending on the model and design of the vehicle. The remaining exhaust gas is pushed out by the piston as it moves back upwards. Exhaust stroke: As the piston reaches the bottom, the exhaust valve opens.Power Stroke: As the fuel reaches the end of its combustion, the heat released from combusting hydrocarbons increases the pressure which causes the gas to push down on the piston and create the power output.At the end of this stroke, a spark plug provides the compressed fuel with the activation energy required to begin combustion. Compression stroke: The intake valve is closed, and the piston moves up the chamber to the top.Intake stroke: The piston moves downward to the bottom this increases the volume to allow a fuel-air mixture to enter the chamber.There is an animation of a four-stroke engine and a further explanation of the process below.
The emissions of carbon monoxide (CO), hydrocarbons (HC) were condensed and a nitrogen oxide (NOx) was amplified for hydrogen compared to gasoline engine operation.The four-stroke engine is the most common type of internal combustion engine and is used in various automobiles that specifically use gasoline as fuel like cars, trucks, and some motorbikes.Ī four-stroke engine delivers one power stroke for every two cycles of the piston (or four-piston strokes). The net heat release rate is enhanced with neat hydrogen engine operation compared to gasoline. In-cylinder pressure is notably increased with hydrogen and peak pressure was shifted towards TDC in comparison with gasoline engine operation. The experimental study discovered the decrement in brake power along with volumetric efficiency and increment in brake thermal efficiency with hydrogen fuel engine operation compared to gasoline operation. Tests were carried out by using pure gasoline and pure hydrogen by different loads and speeds at static ignition timing of 5-degree crank angle before top dead center (deg. This article explores the investigation on combustion, performance and emission characteristics of four-cylinder, four-stroke spark ignition (SI) engine experimentally. Among the several options considered today, hydrogen conceivably the ideal fuel in view of its immeasurable clean-burning qualities, source availabilities and thus promises to be the greatest potential fuel. In respect of depletion of fossil fuel and its harmful effect on the environment, research on alternative fuel engines has fascinated large attention from the engine society.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
